Pump cavitation is a persistent issue that affects many industries around the world. Today we will explore its causes, effects, and best mitigation strategies.
Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge needed to safeguard your pumping systems against the destructive forces of cavitation.
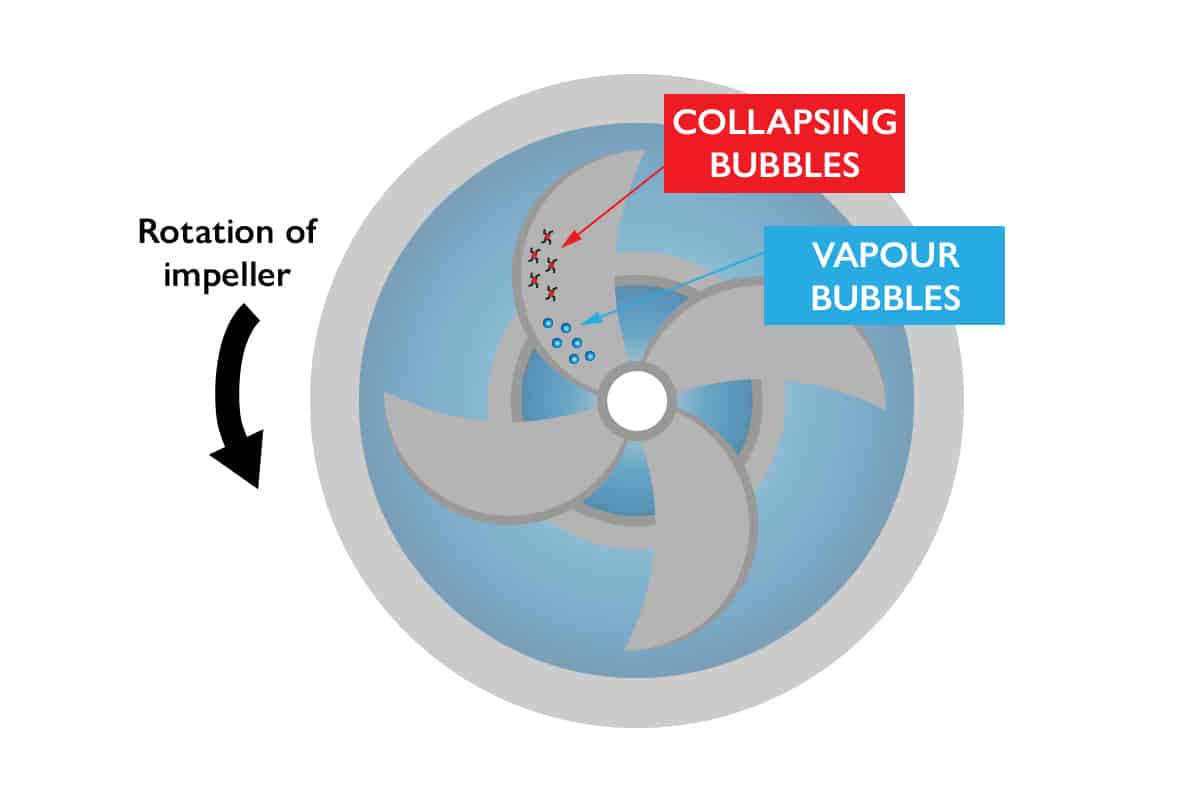
Pump cavitation is defined as the formation and collapse of vapour bubbles within a liquid due to low pressure conditions.
Its impact can have detrimental effects on pump performance, efficiency, and longevity. Therefore, understanding the mechanics of cavitation is crucial for maintaining the reliability and effectiveness of pumping equipment.
As temperature increases, so does the vapour pressure of the liquid. When the pressure at the inlet of a pump falls below the vapour pressure of the liquid being pumped, it creates conditions conducive to cavitation.
This occurs because the liquid is no longer able to withstand the reduced pressure, causing it to vaporise and form bubbles.
Improper inlet conditions can significantly contribute to the occurrence of cavitation.
Low pressure at the pump inlet, often referred to as insufficient Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH), can lead to cavitation by causing the liquid to vaporise as it enters the pump.
Additionally, air entrainment (where air is mixed with the liquid) can exacerbate cavitation problems. Air pockets within the liquid can collapse violently, triggering cavitation even under conditions where the liquid’s vapour pressure is not exceeded.
The properties of the liquid being pumped, such as viscosity and temperature, play a significant role in determining its susceptibility to cavitation.
Higher viscosity fluids are less prone to cavitation due to their greater resistance to vapour bubble formation and collapse. Conversely, lower viscosity fluids are more susceptible to cavitation, as they are more likely to vaporise under reduced pressure conditions.
Inadequate suction piping or excessive restrictions in the inlet flow path can create areas of low pressure, promoting cavitation.
Similarly, improper impeller design or clearance can lead to uneven flow patterns and pressure differentials within the pump, increasing the likelihood of cavitation occurrence.
Finally, pumps operating at off-design conditions (such as low flow rates or high speeds) may also experience cavitation due to the deviation from their optimal operating parameters.
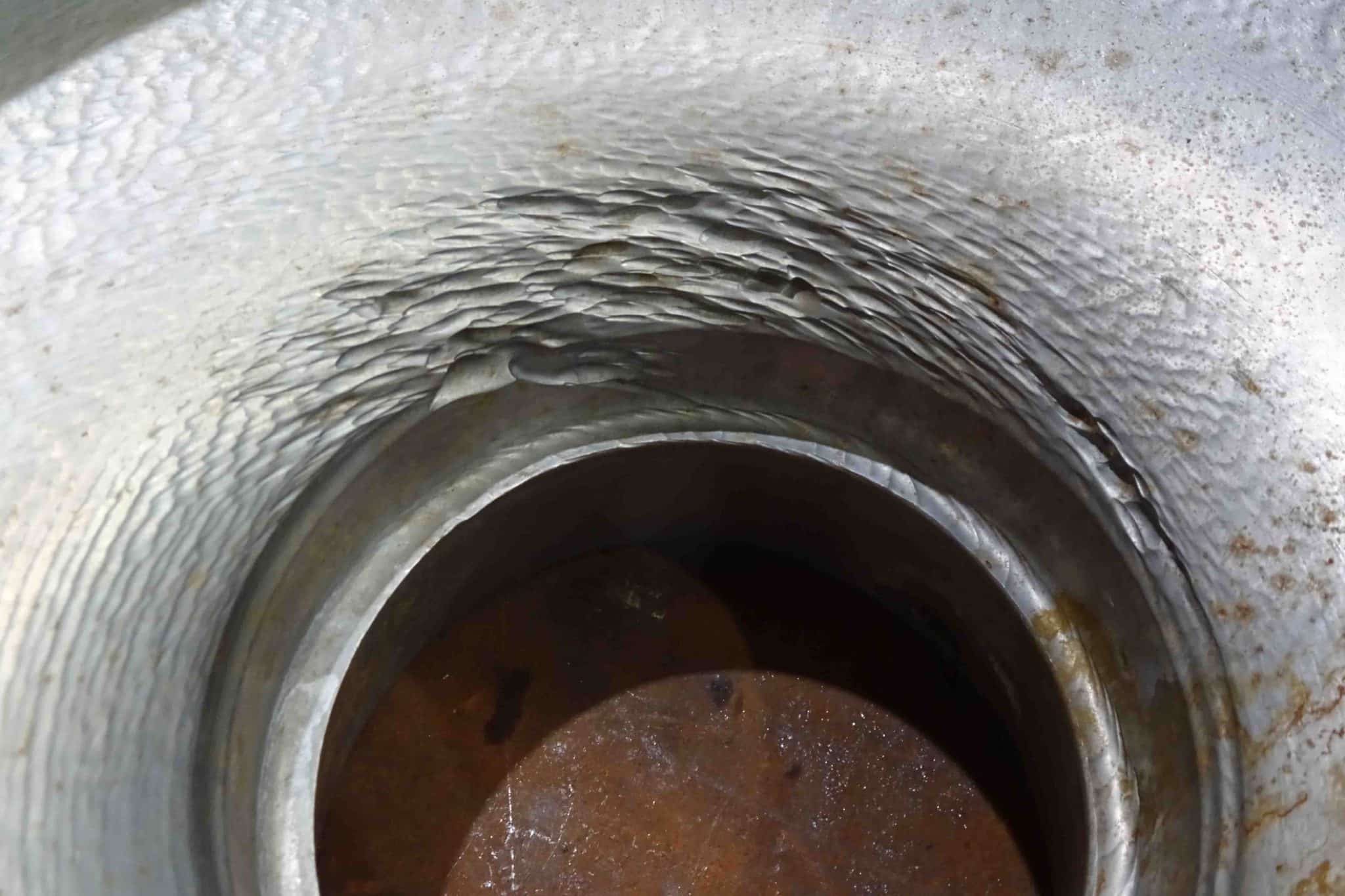

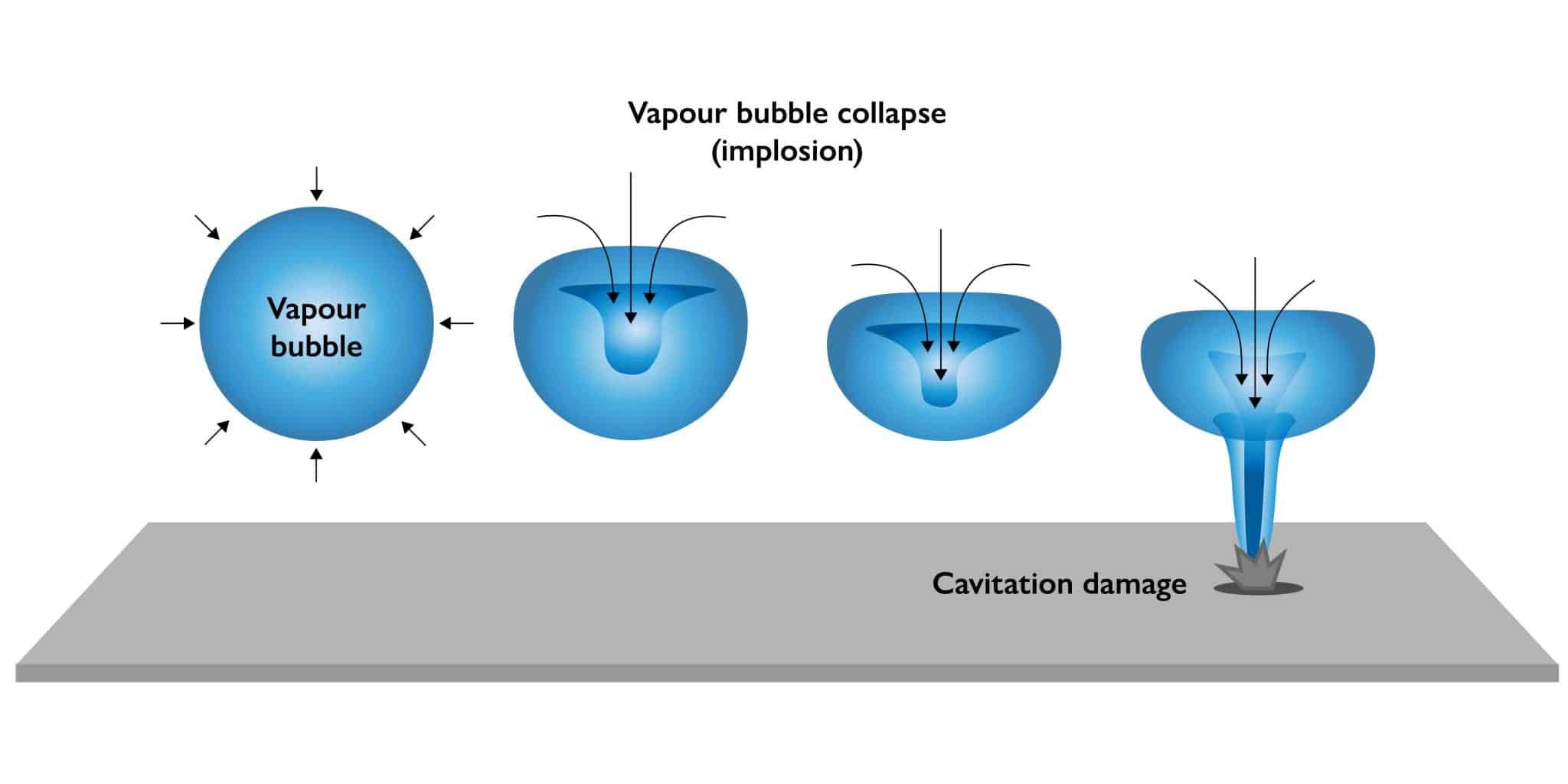
Cavitation-induced pressure fluctuations within a pump can wreak havoc on its internal components, leading to extensive mechanical damage.
As vapour bubbles collapse near solid surfaces, they generate intense shock waves and high-speed liquid jets. These forces can cause erosion, pitting, and surface deterioration on impeller blades, pump casing, and other critical components.
Over time, this erosion can compromise the structural integrity of the pump and reduce its operational lifespan.
Beyond causing mechanical damage, cavitation can also impair the overall efficiency and performance of a pump system.
The formation and collapse of vapour bubbles disrupt the smooth flow of liquid through the pump, leading to flow instabilities and hydraulic inefficiencies.
As a result, the pump’s capacity to deliver the desired flow rate and pressure is compromised, leading to reduced system performance.
One of the most noticeable effects of cavitation is the generation of noise and vibration within the pump system.
As vapour bubbles collapse with tremendous force, they produce audible acoustic emissions that manifest as loud noise levels.
Moreover, cavitation-induced vibrations can propagate through the pump structure and surrounding piping, causing mechanical stress and fatigue.
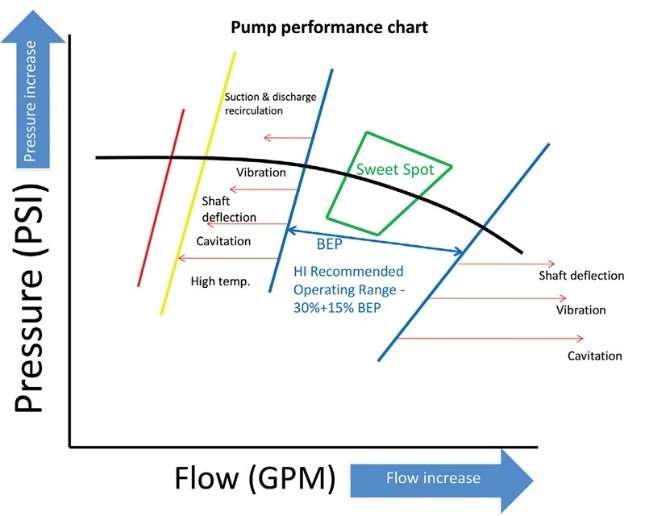
Maintaining appropriate pressure levels within the pump system is critical for preventing cavitation. Ensuring that the pump operates within its designated pressure range helps avoid situations where the pressure at the inlet falls below the vapour pressure of the fluid.
This can be achieved through proper system design, including the use of pressure relief valves, throttling devices, and pressure sensors to regulate and monitor system pressure levels.
Optimizing inlet conditions is crucial for preventing cavitation at the suction side of the pump.
This involves implementing strategies to maintain adequate Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) and minimise air entrainment.
Proper suction piping design, including sufficient diameter and length, helps ensure a smooth and uniform flow of liquid into the pump, reducing the risk of pressure drops and cavitation.
Installing inlet devices such as vortex breakers and strainers can also help improve flow stability and remove entrained air, further mitigating cavitation risks.
Managing liquid properties effectively can significantly reduce the likelihood of cavitation occurrence.
Controlling temperature to maintain the fluid within its operating range helps regulate vapour pressure and minimise cavitation risk.
Measures such as filtration and degassing can also help remove impurities and entrained air from the liquid, improving its cavitation resistance.
Finally, adjusting fluid viscosity through additives or temperature control can also mitigate cavitation effects by altering the fluid’s behaviour under varying operating conditions.
Engineers must carefully consider factors such as flow rate, head, fluid properties, and operating conditions when choosing a pump.
It’s essential to ensure that the selected pump can operate within the specified pressure and flow range without exceeding the fluid’s vapour pressure.
Additionally, choosing pumps with robust design features and materials resistant to cavitation-induced damage can further enhance system reliability and longevity.

If you are unsure about what industrial pump you need to avoid cavitation, please contact us. We will give you an honest recommendation to get your pump operations running efficiently and effectively.
Allied Pumps provides pumping equipment for all sectors including mining, commercial, industrial, and environmental. Explore our range today and get in touch with our team for tailored solutions to your pumping needs.

Contact us to learn about how we can help you with your pump needs.
CALL US NOW EMAIL US